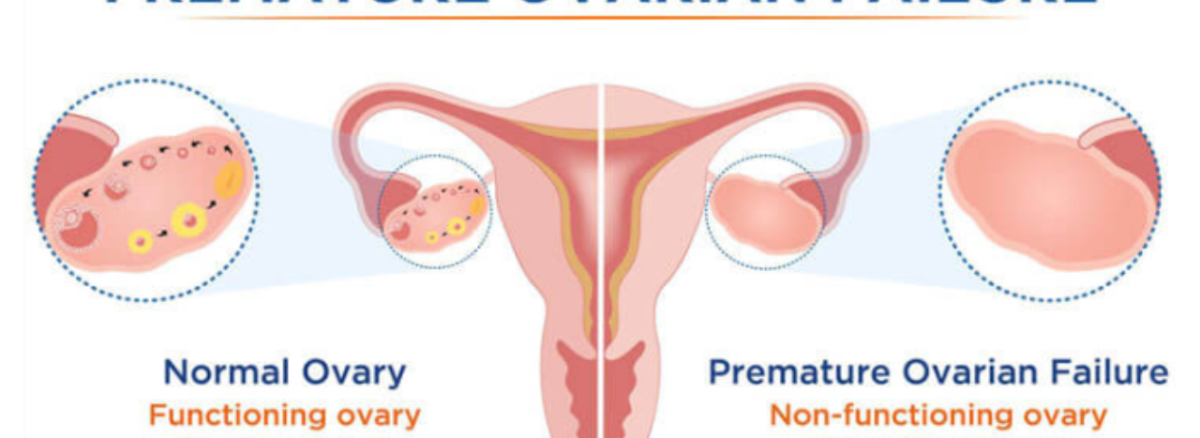
Premature ovarian failure [POF] occurs when the ovary fails to produce
eggs or estrogen in a woman younger than 40 years. This leads to
infertility and abnormal menstrual patterns.
The normal ovarian function is to produce hormones [estrogen,
progesterone, and androgens] and release eggs [ovulation] from the
follicles every month. Ovulation occurs in response to stimulation by the
hypothalamus and pituitary glands.
TYPES OF OVARIAN FAILURE
1. PRIMARY OVARIAN INSUFFICIENCY
This occurs when the ovary fails to function normally in response to
appropriate gonadotropin stimulation provided by the higher centers
[hypothalamus and pituitary]. Hence, there is a primary problem with
the ovaries.
Causes include:
idiopathic causes [ cause not known]
Genetic disorders such as Fragile X syndrome and Turner syndrome.
A low number of follicles.
Autoimmune diseases, including thyroiditis and Addison disease.
Chemotherapy or radiation therapy to treat cancers.
Metabolic disorders.
Toxins, such as cigarette smoke, chemicals, and pesticides.
2. SECONDARY OVARIAN INSUFFICIENCY
This occurs when the hypothalamus and pituitary fail to provide
appropriate gonadotropin stimulation. Hence, the problem is with the
higher centers
Causes include:
Weight loss from eating disorders, chronic disease, and extreme
exercise
Drugs used in cancer treatment [The three most commonly used
drugs, cyclophosphamide, cisplatin and doxorubicin]
Tumors in the Pituitary glands which secrete hormones
Pituitary necrosis where all the pituitary hormones are extremely low
(Sheehan syndrome)
Hypothalamic tumor which causes a dysfunction of the organ
The risk of POF is higher in persons with a family history of the same and
surgeries involving the ovary.
SYMPTOMS
A lady with ovarian insufficiency may have no initial symptoms at the initial
stage.
The earliest symptom noticeable is short or irregular menses. This could
occur following the use of oral contraceptive pills. Other symptoms are
similar to those of menopause and include:
Night sweats
Hot flushes
Poor memory
Vaginal dryness
Mood swings
Inability getting pregnant
PREVENTION
If the cause of the ovarian failure is known the client can be counseled to
avoid factors that could trigger the condition such as weight gain, reducing
exercises and avoiding medications which could lead to it.
LONG TERM CHALLENGES
It is important to make an early diagnosis of premature ovarian failure to
avoid severe health challenges in this group of women. Apart from
Infertility, a client with POF present with:
Increased risk of bone fracture.
This is caused by low estrogen levels, thereby leading to weak bones
which can fracture easily.
Increased risk of heart disease
Estrogen protects the heart from heart diseases. Early loss of
estrogen predisposes women to heart problems
DIAGNOSIS
Diagnosing POF usually begins with a history of the above symptoms:
menstrual irregularity, chronic illness, drug use, exercise, poor eating
habits or disorders.
1. Laboratory tests
Hormonal assay to assess the level of serum Follicle-Stimulating
Hormone [FSH], Luteinizing Hormone [LH] and Estradiol on day 3 of
menses.
Level of Anti-Mullerian Hormone [AMH] which checks for the level of
remaining follicles. These levels are low.
2. An ultrasound scan of the ovary may reveal small, shrunken ovaries.
3. MRI of the brain [hypothalamus and pituitary] may be useful where a
tumor of the pituitary gland is suspected.
TREATMENT
There is usually no treatment available to restore ovarian function when
the challenge is a primary ovarian failure with the challenge at the level of
the ovaries.
For secondary ovarian failure, it may be possible to reverse the challenge
depending on the cause of the problem.
1. Lifestyle changes
Women are counseled to perform weight-bearing exercises and take
calcium supplements because of the risk of bone fractures.
For those interested in having children, options such as the use of donor
eggs, and adoption should be discussed with them. However, about 5 % of
these women may get pregnant spontaneously.
2. Medical Treatment
Women benefit from estrogen therapy to help protect the heart from
diseases and the bones from fractures.
Progesterone medications can be given also to help the client menstruate
each month, thus preventing endometrial hyperplasia and reducing the risk
of endometrial cancers.