INTRODUCTION
An ectopic pregnancy occurs when the pregnancy grows outside the uterus. Ectopic means ‘out of place’. It is one of the obstetric emergencies and a cause of maternal mortality. It occurs in 1 % of pregnancies; however, its incidence is higher when a client has fertility treatment.
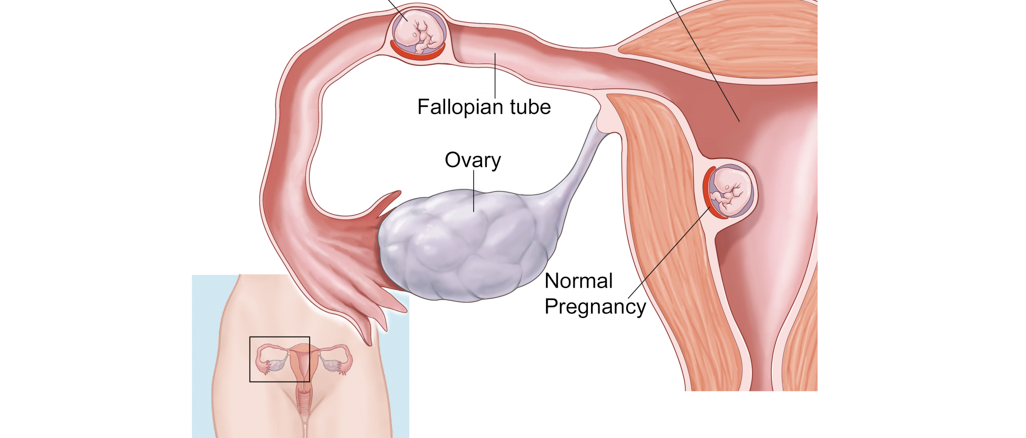
Ectopic pregnancies could implant in the fallopian tube [commonest site], ovary, abdomen, and cervix. Occasionally a client could have a pregnancy in the tube and the uterus at the same time [heterotopic pregnancy].
SYMPTOMS
A lady with an ectopic pregnancy may present with abdominal pains and vaginal bleeding. Following the rupture of the fallopian tube, severe intra-abdominal bleeding could occur and she could get dizzy and faint, presenting with a fast heart rate and decreased blood pressure. If this continues with no medical attention, the client could die.
CAUSES
Risks of ectopic pregnancies are high in:
- Persons with abnormally long fallopian tubes
- Previous history of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
- Use of IVF
- Previous History of surgery in the tubes
- Previous history of ectopic pregnancy
- Use of emergency contraception, such as Postinor 2 around the time of ovulation
- Smokers
PREVENTION
The risk of ectopic pregnancy rupturing could be reduced by having an ultrasound scan done when the lady misses her period. The Ultrasound scan helps determine the location of the pregnancy, hence interventions can be carried out promptly.
DIAGNOSIS
In many cases, the diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy is a dilemma. However, a diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy should be considered in every woman of reproductive age who has abdominal pains and a pregnancy test result that is positive.
A transvaginal scan should also be carried out which may reveal a pregnancy in the fallopian tube. If there is no pregnancy in the tube and the pregnancy test is positive, a serum Beta HCG would be done to help differentiate it from an ongoing small intrauterine pregnancy.
A laparoscopy could also be carried out to make a diagnosis. It involves inserting a laparoscope through the abdomen to visualize the ectopic pregnancy.
TREATMENT
Medical Treatment: Involves the use of methotrexate injection for unruptured ectopic pregnancy.
Surgery: Involves the removal of the damaged tube through a salpingectomy. This could be carried out through Laparoscopy [involves the use of pinhole incisions with the aid of a camera to access the abdominal cavity] or Laparotomy [involves making a large incision through the abdominal wall to gain access into the cavity].
Laparoscopy is the favoured option of management as it is minimally invasive and reduces the risk of adhesions among other benefits.
WHEN TO SEE A DOCTOR
- If you have missed your period and notice you have abdominal pains, you should see your doctor and have a pregnancy test and an ultrasound scan.
- If you had a previous history of ectopic pregnancy, you should see your doctor anytime you miss your period.
- If you have a mother or sister who has breast cancer or died from it you should book an appointment with your doctor.

1 Comment