INTRODUCTION
The endometrium is the inner lining of the uterus that gets shed off during the monthly menses. It prevents the walls of the womb from fusing.
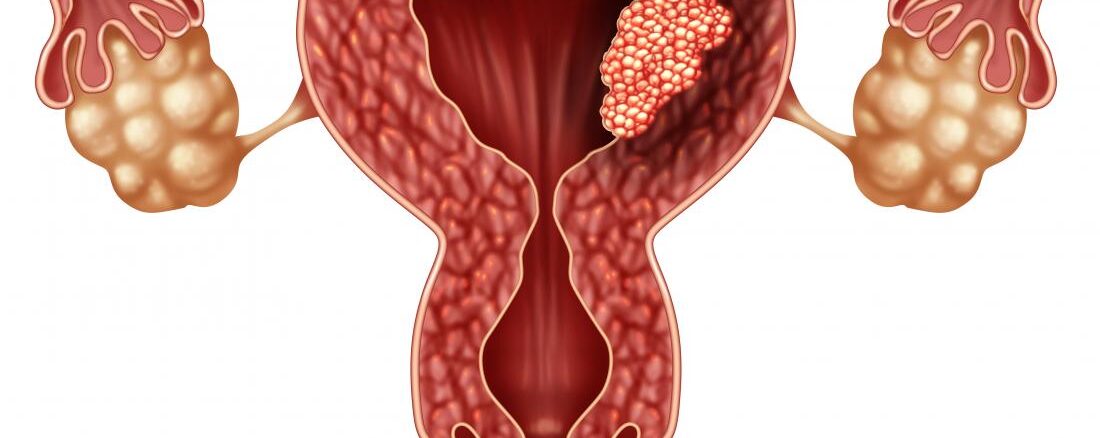
Endometrial cancer affects this lining of the uterus [womb], unlike cervical cancer that affects the cervix [neck of the womb]. It is one of the most common cancers in developed countries. In Nigeria, it is not as common as possible because of our life expectancy. It occurs more in women in their 60s although some women develop it earlier.
SYMPTOMS
Most women will present with postmenopausal bleeding. This is the resumption of fresh bleeding after they have stopped bleeding for up to one year.
For other women, frequent heavy menses or bleeding in between your period should make you visit your gynaecologist.
Some women will present with pelvic pain.
CAUSES
There is no known cause for endometrial cancer; however, several factors have been identified in clients with the disease
- Family history: Women with a family member diagnosed with endometrial cancer have an increased risk of developing the disease themselves. Some of these families also have a risk of developing colon cancer.
- ii. Overweight women: This may be because excess body fat gets converted to estrogen which acts on the endometrium.
iii. Childlessness: Infertility or volunteering not to have children increases the risk of endometrial cancer by increasing the number of menstrual cycles.
- Anovulation: This occurs when women do not ovulate. This occurs in conditions such as Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome [PCOS].
- Age: The risk of endometrial cancer rises with age.
- Diet high in fat: These diets have a large calorie dose that leads to obesity which is a risk factor.
vii. History of endometrial hyperplasia: Endometrial hyperplasia is a condition in which there is increased growth of the endometrium possibly from irregular menstruation. It poses a risk if not treated.
viii. Use of HRT [Hormone Replacement Therapy]: Its use to treat menopausal symptoms with estrogen alone increases the risk.
PREVENTION
Although most cases of endometrial cancers may not be preventable, the following could help reduce your risk of developing endometrial cancer.
- Weight reduction and an active lifestyle
- Use of combined oral contraceptive pills for at least 1 year
- Having children
- Getting treated for abnormal vaginal bleeding
- If you have to use hormone replacement therapy for menopausal symptoms, ensure your doctor adds a progestin to counteract the effect of estrogen.
DIAGNOSIS
Investigations needed for diagnosis include radiological tests and biopsy.
Transvaginal Ultrasound Scan
Your doctor uses a transvaginal scan to check the thickness of the endometrium. If the thickness is much larger than normal for the age of the woman and phase of her menstrual period further tests are carried out.
Sonohysterogram
This involves inserting fluid into the uterus and then carrying out a transvaginal scan. This procedure helps distend the uterus and makes problems within the uterus easy to see.
Endometrial Biopsy
This involves taking a specimen from the lining of the womb and sending it to the laboratory for evaluation. It is a blind procedure and areas with challenges can be missed.
Hysteroscopically directed biopsy
This method involves using a camera and light source to look into the uterus. It is more accurate and areas that look diseased can be biopsied.
TREATMENT
Surgery
This involves total abdominal hysterectomy [removal of the uterus and cervix], bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy [removal of the ovaries and fallopian tubes], peritoneal cytology and pelvic and para-aortic lymphadenectomy. This way most of the cancer cells and areas it has spread to are reduced.
Chemotherapy
Cisplatin is the major medication for cancer treatment. It discourages the growth and spread of cancer cells.
WHEN TO SEE A DOCTOR
- If you are postmenopausal [you have stopped menstruating and notice you start bleeding again]
- If you are still menstruating and notice a change in your menstrual pattern such as heavier flow, bleeding in between menses for more than 1 cycle