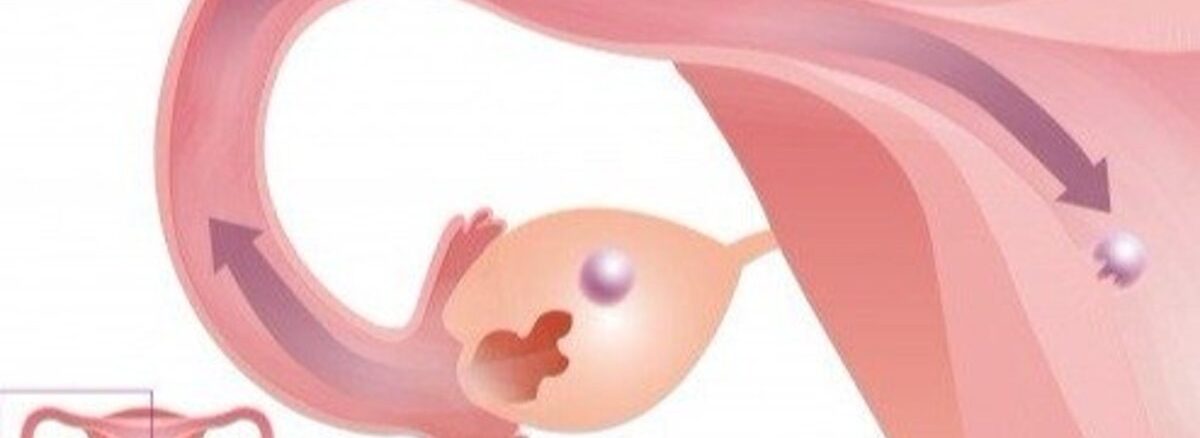
Eggs are naturally present in the ovaries [follicles] of a woman and every month one of them matures and gets released resulting in ovulation. This released egg is picked up by the fimbriae of the fallopian tube and travels within the tube where it gets fertilized with a sperm cell if present.
Ovulation induction drugs could be used to increase the number of eggs released at the time of ovulation from the ovaries and hence improve the chances of pregnancy occurring. It can be combined with any of the procedures such as IUI, IVF, ICSI.
These drugs act by causing an increased release of hormones such as follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH).
An increase in FSH influences the growth and maturation of multiple ovarian follicles. A surge in LH by the pituitary gland helps with the final maturation of the egg and leads to ovulation 36-40 hours after its initiation.
There are several types of medications that can be used to stimulate the ovaries which are described below.
-
CLOMIPHENE CITRATE [CLOMID]
This is an anti-estrogen medication that acts by increasing the levels of FSH and stimulating the development of follicles. It is taken by mouth usually for five days starting from day 3 – 5 of the menses. Dosage is 50 -150 mg daily. It is preferably taken at night to reduce its unwanted effects.
Common unwanted effects include-, headaches, hot flushes, visual changes, ovulation pains, mood changes.
-
LETROZOLE [FEMARA]
This is an aromatase inhibitor that helps to suppress estrogen production leading to an increase in FSH. FSH increase stimulates the ovaries to produce multiple follicles thus increasing the chances of pregnancy.
It is taken by mouth usually for five days starting from day 3 – 5 of the menses. Dosage is 2.5 -5 mg daily. It is preferably taken at night to reduce its unwanted effects.
Common unwanted effects include-, headaches, hot flushes, muscle ache, diarrhoea, dizziness, ovulation pains, mood changes.
-
GONADOTROPINS
These are injectable drugs that cause the ovaries to produce multiple follicles and eggs. They are usually given daily from the 2nd or 3rd day of commencement of menses and are stopped when the eggs are large enough for ovulation to occur. They are administered subcutaneously, under the skin.
Several types of gonadotropins are available and include:
- FSH only [Gonal F and Bravelle]
- Human Menopausal Gonadotropin, a combination of FSH and LH [Menopur]
Common unwanted effects include- weight gain, leg swelling, nausea and vomiting, severe lower abdominal pains.
-
HUMAN CHORIONIC GONADOTROPINS [PREGNYL]
These are injectable drugs that cause the ovaries to release the eggs and cause ovulation to occur. They are similar in action to LH. They are given when the size of the follicles containing the eggs are large enough for ovulation to occur. After administration of HCG, ovulation occurs in 36 – 40 hours.
Common unwanted effects include-, headaches, irritability, leg swelling, depression, pain at the injection site and restlessness.
OTHER USEFUL MEDICATIONS
-
GONADOTROPINS RELEASING HORMONE [GNRH] ANTAGONIST [CETROTIDE]
These are injectable drugs that help prevent premature ovulation from occurring. It gives the physician control over the timing of your ovulation so the IUI procedure can be timed around the time of the desired ovulation.
Cetrotide can be given subcutaneously as 0.25 mg daily doses or a single shot of 3 mg. It is commenced when the largest follicle is about 14 mm during the process of stimulation and stopped before the HCG trigger is given.
Common unwanted effects include headaches, nausea, and pain at the injection site.
-
GONADOTROPINS RELEASING HORMONE [GNRH] AGONIST [LUPRON]
These are injectable drugs that help prevent ovulation from occurring naturally. It gives the physician control over the timing of your ovulation so the IUI procedure can be timed around the time of ovulation.
Lupron is given subcutaneously as 0.1 ml daily from the 21st day of the last menses and stopped before the HCG trigger is given.
Common unwanted effects include headaches, increased sweating, tiredness, nausea and vomiting, hot flushes, pain at the injection site.
INDICATIONS FOR OVULATION INDUCTION
Ovulation induction is recommended for women with:
- Polycystic ovary syndrome(PCOS)
- Anovulatory cycles [not ovulating]
- Hormonal imbalance
- Unexplained infertility [infertility with no known cause]
- Irregular menstrual pattern
HOW TO ADMINISTER SUBCUTANEOUS INJECTION
- Choose injection site which could be the outer side of the upper thigh, back of upper arm or fold of abdomen below the umbilicus.
- Swab the area of skin with alcohol and allow drying.
- When the site is dry, pinch a fold of skin and use your other hand to insert the needle straight into the injection site.
- Release the pinch and slowly depress the plunger all the way and remove the needle.
- Use a clean gauze pad to stop any bleeding that may occur.